TensorBoard简单使用
介绍
在介绍TensorBoard之前,首先聊一聊它与它兄弟的关系,即TensorBoardX。
在PyTorch刚发布时,不支持TensorBoard可视化工具。GitHub用户lanpa开发了TensorBoardX,一个完全支持PyTorch的TensorBoard工具包。
PyTorch官方对TensorBoard的支持是在PyTorch 1.1.0版本中实现的。与TensorBoardX在使用上基本一样,教程也是可以通用的,区别可能仅在于一个是大佬开发的,一个是PyTorch官方与TensoBoard合作的。
对应的导入方式:
1
2
3
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
这篇文章主要以PyTorch官方的TensorBoard为主体介绍。
一些有用的网站:
tensorboardX官方文档:https://tensorboardx.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
B站小土堆的教程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hE411t7RN/?p=8
另一篇简单介绍的文章:https://community.modelscope.cn/63ca6125406cc115977187fa.html
使用TensorBoard的一般流程
初始化 SummaryWriter
以下是三种初始化 SummaryWriter 的方法,在运行使用TensorBoard的代码后会在工作目录下创建文件夹与记录文件,可以手动确定要使用的路径或者自动生成:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# 手动确定要使用的路径
# 记录会保存在 './runs/exp'
writer1 = SummaryWriter('runs/exp')
# 自动生成
# 记录会保存在类似这样的文件夹 './runs/Aug20-17-20-33'
writer2 = SummaryWriter()
# 加入注释
# 记录会保存在类似这样的文件夹 'runs/Aug20-17-20-33-resnet'
writer3 = SummaryWriter(comment='resnet')
写入不同类型的数据
这一小节的任务是熟悉一般流程,在这里使用最简单的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter()
for i in range(100):
writer.add_scalar('y=2x', i*2, i)
writer.add_scalar('y=pow(2,x)', 2**i, i)
writer.close()
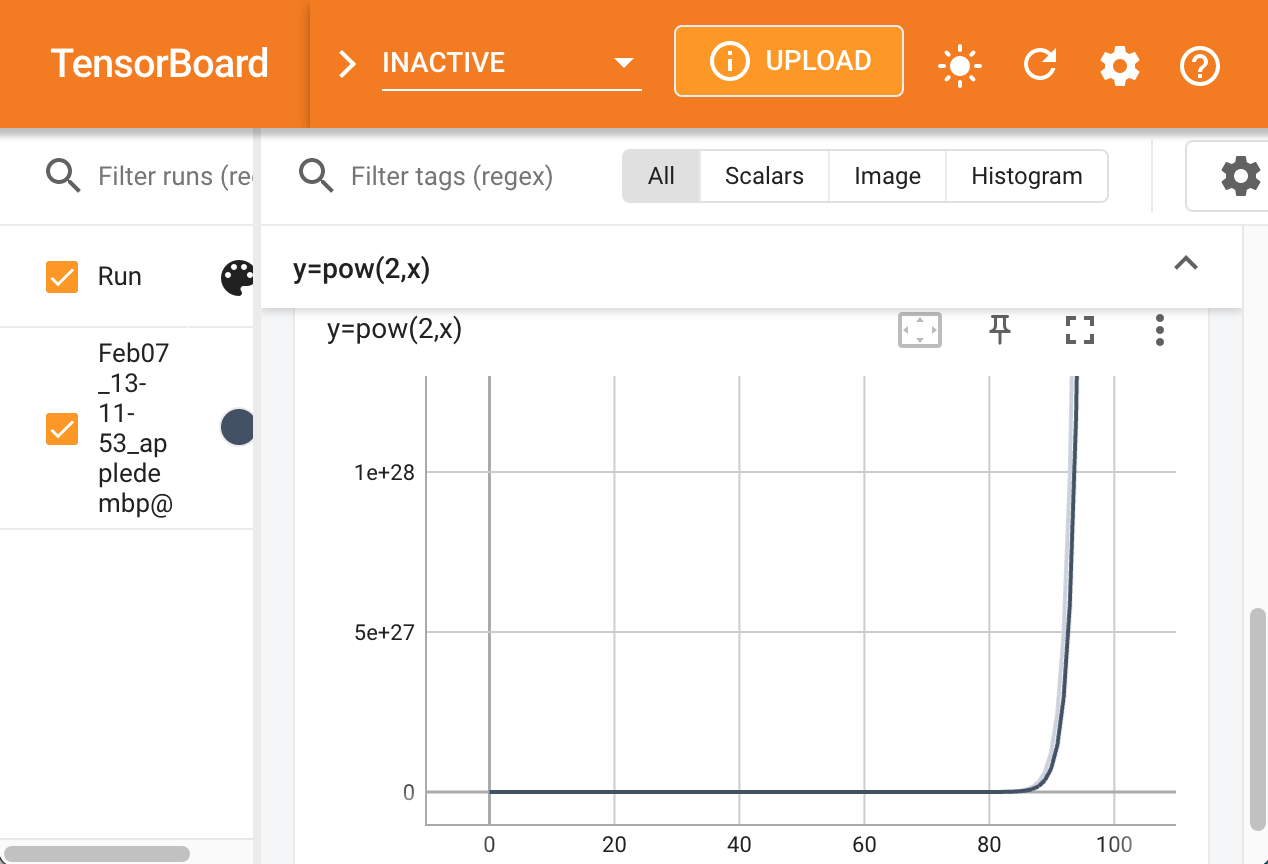
在上面的代码中,我们初始化了一个SummaryWriter,并且写入了一些标量,这些标量可以组成函数曲线。现在运行代码,注意运行代码不会发生任何事,但是会在自动生成的文件夹runs中留下记录文件。
打开可视化面板
在工作目录下打开终端输入命令:
1
tensorboard --logdir runs
会有一些输出,提示你打开网页http://localhost:6006/ ,打开链接,你会看到曲线已经画在浏览器网页上了。
补充:命令的一般格式: tensorboard --logdir [目录] --port [端口号]。 tensorboard会递归寻找目录下的所有文件,如果不想显示所有记录文件,建议使用更具体的目录名,并且定期清理不需要的记录文件。可以另外制定端口号避免冲突。
常见方法速查
标量
- 添加标量
add_scalar(self, tag, scalar_value, global_step=None, walltime=None) - 添加标量组
add_scalars(self, main_tag, tag_scalar_dict, global_step=None, walltime=None) - 输出标量
export_scalars_to_json(self, path) add_custom_scalars_multilinechart(self, tags, category='default', title='untitled')add_custom_scalars_marginchart(self, tags, category='default', title='untitled')add_custom_scalars(self, layout)
图像图表
- 添加直方图
add_histogram(self, tag, values, global_step=None, bins='tensorflow', walltime=None)记录直方图很耗CPU 资源,不要常用 - 添加图像
add_image(self, tag, img_tensor, global_step=None, walltime=None, dataformats='CHW') - 添加图像组
add_images(self, tag, img_tensor, global_step=None, walltime=None, dataformats='NCHW') add_image_with_boxes(self, tag, img_tensor, box_tensor, global_step=None,walltime=None, dataformats='CHW', **kwargs)- 将matplotlib图形渲染成图像并将其添加到摘要中
add_figure(self, tag, figure, global_step=None, close=True, walltime=None) - 添加网络图形
add_graph(self, model, input_to_model=None, verbose=False, **kwargs)
精度曲线
- 添加精度曲线
add_pr_curve(self, tag, labels, predictions, global_step=None,num_thresholds=127, weights=None, walltime=None)pr:precision-recall - 使用原始数据添加精确调用曲线
add_pr_curve_raw(self, tag,true_positive_counts,false_positive_counts,true_negative_counts,false_negative_counts,precision, recall,global_step=None,num_thresholds=127,weights=None, walltime=None)
音频/视频/文字/嵌入
- 添加音频
add_video(self, tag, vid_tensor, global_step=None, fps=4, walltime=None) - 添加视频
add_audio(self, tag, snd_tensor, global_step=None, sample_rate=44100, walltime=None) - 添加文本
add_text(self, tag, text_string, global_step=None, walltime=None) add_embedding(self, mat, metadata=None, label_img=None, global_step=None, tag='default', metadata_header=None)
参数释义
- tag: 标签,数据标识符号,名称(string):
- main_tag:标签组名称(string)
- tag_scalar_dict:标签键值对,(dict);
- scalar_value : 要保存的值
(float or string/blobname) - global_step : 要记录的全部步长值(int)
- walltime (float):
Optional override default walltime (time.time()) of event可选覆盖默认的walltime(time.time()),以秒为单位事件的时期 - dataformats:CHW(默认),NCHW(默认),HW,NHWC
- img_tensor (torch.Tensor, numpy.array, or string/blobname): 默认shape为(3,H,W)。可以使用torchvision.utils.make_grid()将一批张量转换为3xHxW格式或调用
add_images完成。也可以设置为(1,H,W)、(H,W)。为避免出错,建议使用默认值CHW(channel在前,更符合一般习惯),img_tensor需要和dataformats匹配。 - model (torch.nn.Module): 添加模型图graph
- input_to_model (torch.Tensor or list of torch.Tensor): 喂入模型的数据.
网络结构可视化
也许TensorBoard最不可替代的功能是使神经网络结构可视化,我们用几个简单的例子介绍。
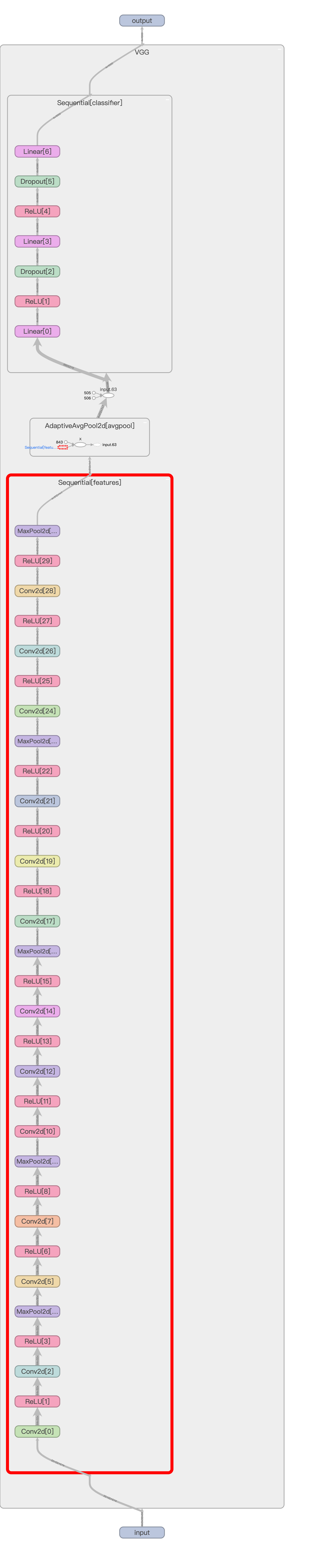
可视化VGG16网络
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import torch
from torchvision.models import vgg16
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
net = vgg16() # 实例化网络
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 32, 32) # 随机张量作为输入
with SummaryWriter(log_dir='') as sw:
sw.add_graph(net, x) # 参数为神经网络和输入
sw.close()
TensorBoard得到如下的网络结构:
可视化自定义网络
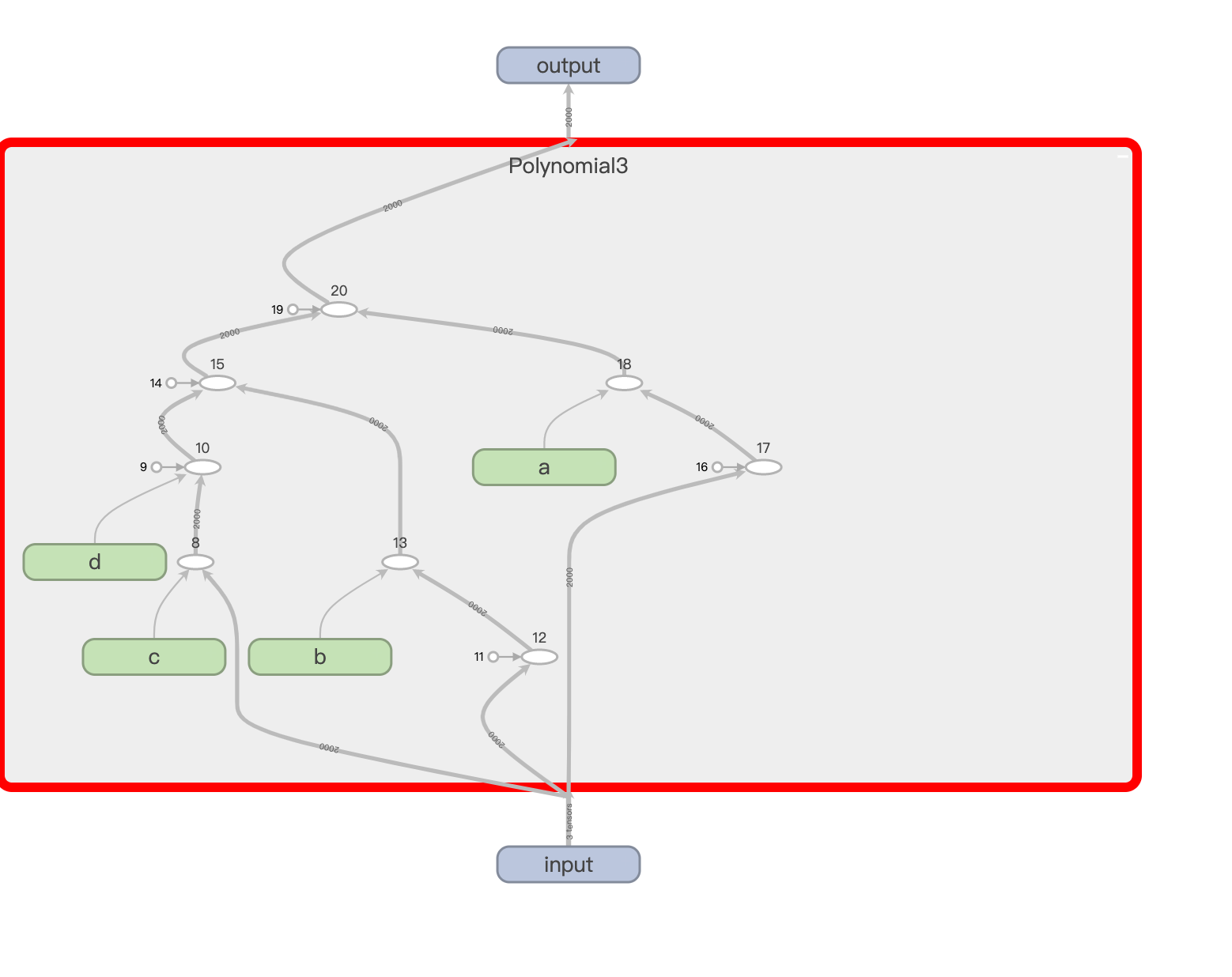
第一个例子是我们之前的实战例子,复习一下,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
import torch
import math
class Polynomial3(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.a = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(()))
self.b = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(()))
self.c = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(()))
self.d = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(()))
def forward(self, x):
return self.d + self.c * x + self.b * x ** 2 + self.a * x ** 3
def string(self):
return f'y = {self.d.item()} + {self.c.item()} x + {self.b.item()} x^2 + {self.a.item()} x^3'
x = torch.linspace(-math.pi, math.pi, 2000)
y = torch.sin(x)
model = Polynomial3()
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-6)
for t in range(2000):
y_pred = model(x)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y)
if t % 100 == 0:
print(t, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f'Result: {model.string()}')
我们加上一点内容:
1
2
3
4
5
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
with SummaryWriter() as sw:
sw.add_graph(model, x)
sw.close()
得到网络结构:
第二个例子来自官方教程,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
# imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# helper function to show an image
# (used in the `plot_classes_preds` function below)
def matplotlib_imshow(img, one_channel=False):
if one_channel:
img = img.mean(dim=0)
img = img / 2 + 0.5 # unnormalize
npimg = img.numpy()
if one_channel:
plt.imshow(npimg, cmap="Greys")
else:
plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0)))
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5) # 图像现在是一个通道而不是三个通道,是28x28而不是32x32
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 4 * 4, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 4 * 4)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
# transforms
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))
])
# datasets
trainset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST('./data',
download=True,
train=True,
transform=transform)
testset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST('./data',
download=True,
train=False,
transform=transform)
# dataloaders
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=4,
shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=4,
shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
# constant for classes
classes = ('T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle Boot')
net = Net()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# default `log_dir` is "runs" - we'll be more specific here
writer = SummaryWriter('runs/fashion_mnist_experiment_1')
# get some random training images
dataiter = iter(trainloader)
images, labels = next(dataiter)
# create grid of images
img_grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)
# show images
matplotlib_imshow(img_grid, one_channel=True)
# write to tensorboard
writer.add_image('four_fashion_mnist_images', img_grid)
writer.add_graph(net, images)
writer.close()
输出的网络结构类似,请打开网页自行查看。
更多例子
这个例子来源于TensorBoardX官方demo,GitHub页面链接:https://github.com/lanpa/tensorboardX
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# demo.py
import torch
import torchvision.utils as vutils
import numpy as np
import torchvision.models as models
from torchvision import datasets
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
resnet18 = models.resnet18(False)
writer = SummaryWriter()
sample_rate = 44100
freqs = [262, 294, 330, 349, 392, 440, 440, 440, 440, 440, 440]
for n_iter in range(100):
dummy_s1 = torch.rand(1)
dummy_s2 = torch.rand(1)
# data grouping by `slash`
writer.add_scalar('data/scalar1', dummy_s1[0], n_iter)
writer.add_scalar('data/scalar2', dummy_s2[0], n_iter)
writer.add_scalars('data/scalar_group', {'xsinx': n_iter * np.sin(n_iter),
'xcosx': n_iter * np.cos(n_iter),
'arctanx': np.arctan(n_iter)}, n_iter)
dummy_img = torch.rand(32, 3, 64, 64) # output from network
if n_iter % 10 == 0:
x = vutils.make_grid(dummy_img, normalize=True, scale_each=True)
writer.add_image('Image', x, n_iter)
dummy_audio = torch.zeros(sample_rate * 2)
for i in range(x.size(0)):
# amplitude of sound should in [-1, 1]
dummy_audio[i] = np.cos(freqs[n_iter // 10] * np.pi * float(i) / float(sample_rate))
writer.add_audio('myAudio', dummy_audio, n_iter, sample_rate=sample_rate)
writer.add_text('Text', 'text logged at step:' + str(n_iter), n_iter)
for name, param in resnet18.named_parameters():
writer.add_histogram(name, param.clone().cpu().data.numpy(), n_iter)
# needs tensorboard 0.4RC or later
writer.add_pr_curve('xoxo', np.random.randint(2, size=100), np.random.rand(100), n_iter)
dataset = datasets.MNIST('mnist', train=False, download=True)
images = dataset.test_data[:100].float()
label = dataset.test_labels[:100]
features = images.view(100, 784)
writer.add_embedding(features, metadata=label, label_img=images.unsqueeze(1))
# export scalar data to JSON for external processing
writer.export_scalars_to_json("./all_scalars.json")
writer.close()
想要看看更多网络结构?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torch.autograd import Variable
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
dummy_input = (torch.zeros(1, 3),)
class LinearInLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LinearInLinear, self).__init__()
self.l = nn.Linear(3, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.l(x)
with SummaryWriter(comment='LinearInLinear') as w:
w.add_graph(LinearInLinear(), dummy_input, True)
class MultipleInput(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MultipleInput, self).__init__()
self.Linear_1 = nn.Linear(3, 5)
def forward(self, x, y):
return self.Linear_1(x + y)
with SummaryWriter(comment='MultipleInput') as w:
w.add_graph(MultipleInput(), (torch.zeros(1, 3), torch.zeros(1, 3)), True)
class MultipleOutput(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MultipleOutput, self).__init__()
self.Linear_1 = nn.Linear(3, 5)
self.Linear_2 = nn.Linear(3, 7)
def forward(self, x):
return self.Linear_1(x), self.Linear_2(x)
with SummaryWriter(comment='MultipleOutput') as w:
w.add_graph(MultipleOutput(), dummy_input, True)
class MultipleOutput_shared(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MultipleOutput_shared, self).__init__()
self.Linear_1 = nn.Linear(3, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.Linear_1(x), self.Linear_1(x)
with SummaryWriter(comment='MultipleOutput_shared') as w:
w.add_graph(MultipleOutput_shared(), dummy_input, True)
class SimpleModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleModel, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x * 2
model = SimpleModel()
dummy_input = (torch.zeros(1, 2, 3),)
with SummaryWriter(comment='constantModel') as w:
w.add_graph(model, dummy_input, True)
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
# self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += residual
out = F.relu(out)
return out
dummy_input = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
with SummaryWriter(comment='basicblock') as w:
model = BasicBlock(3, 3)
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,), verbose=True)
class Net1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net1, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(20)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2)
x = F.relu(x) + F.relu(-x)
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
x = self.bn(x)
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = F.softmax(x, dim=1)
return x
class Net2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net2, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return x
dummy_input = Variable(torch.rand(13, 1, 28, 28))
model = Net1()
with SummaryWriter(comment='Net1') as w:
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,))
model = Net2()
with SummaryWriter(comment='Net2') as w:
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,))
class SiameseNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SiameseNetwork, self).__init__()
self.cnn1 = Net1()
def forward_once(self, x):
output = self.cnn1(x)
return output
def forward(self, input1, input2):
output1 = self.forward_once(input1)
output2 = self.forward_once(input2)
return output1, output2
model = SiameseNetwork()
with SummaryWriter(comment='SiameseNetwork') as w:
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input, dummy_input))
dummy_input = torch.Tensor(1, 3, 224, 224)
with SummaryWriter(comment='alexnet') as w:
model = torchvision.models.alexnet()
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,))
with SummaryWriter(comment='vgg19') as w:
model = torchvision.models.vgg19()
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,))
with SummaryWriter(comment='densenet121') as w:
model = torchvision.models.densenet121()
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,))
with SummaryWriter(comment='resnet18') as w:
model = torchvision.models.resnet18()
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,))
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.i2h = nn.Linear(
n_categories +
input_size +
hidden_size,
hidden_size)
self.i2o = nn.Linear(
n_categories +
input_size +
hidden_size,
output_size)
self.o2o = nn.Linear(hidden_size + output_size, output_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, category, input, hidden):
input_combined = torch.cat((category, input, hidden), 1)
hidden = self.i2h(input_combined)
output = self.i2o(input_combined)
output_combined = torch.cat((hidden, output), 1)
output = self.o2o(output_combined)
output = self.dropout(output)
output = self.softmax(output)
return output, hidden, input
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size)
n_letters = 100
n_hidden = 128
n_categories = 10
rnn = RNN(n_letters, n_hidden, n_categories)
cat = torch.Tensor(1, n_categories)
dummy_input = torch.Tensor(1, n_letters)
hidden = torch.Tensor(1, n_hidden)
out, hidden, input = rnn(cat, dummy_input, hidden)
with SummaryWriter(comment='RNN') as w:
w.add_graph(rnn, (cat, dummy_input, hidden), verbose=False)
lstm = torch.nn.LSTM(3, 3) # Input dim is 3, output dim is 3
inputs = [torch.randn(1, 3) for _ in range(5)] # make a sequence of length 5
# initialize the hidden state.
hidden = (torch.randn(1, 1, 3),
torch.randn(1, 1, 3))
for i in inputs:
out, hidden = lstm(i.view(1, 1, -1), hidden)
with SummaryWriter(comment='lstm') as w:
w.add_graph(lstm, (torch.randn(1, 3).view(1, 1, -1), hidden), verbose=True)
import pytest
print('expect error here:')
with pytest.raises(Exception) as e_info:
dummy_input = torch.rand(1, 1, 224, 224)
with SummaryWriter(comment='basicblock_error') as w:
w.add_graph(model, (dummy_input,)) # error